FV2200 can read files on your computer that have been transferred from control units (Procedure 3.1 - Moving Data to a Computer), or directly from an LAI‑2270C Control Unit that is connected to your computer with a USB cable.
To open files that are saved on your computer’s hard drive or the LAI-2200C console if it is attached via USB, click the Open icon or File > Open and navigate to the stored file. Double click the file to open it, or select multiple files and click OK.
Alternatively, you can drag the data file(s) onto the main window: The file(s) will be opened in the current view, or if there are no views, one will be created.
On Mac and Windows operating systems, you can drag and drop the data file(s) onto the FV2200 icon: on Mac, if FV2200 is not running, it will launch, create a view, and open the files in that view. If FV2200 is running, this is just like dropping the files onto the main windows. On Windows, FV2200 will launch (if it is already running, a second one is launched), a view is created, and the files opened in the view.
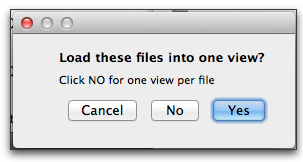
If multiple files were selected, click Yes to place them into one tab or No to place them in separate tabs.
Once files have been opened, a view is created with the tab showing the source files. If you open another file or group of files, these will go into a second view. LAI files (rows of a view) can be cut, copied, and pasted from one view to another.
View an LAI File
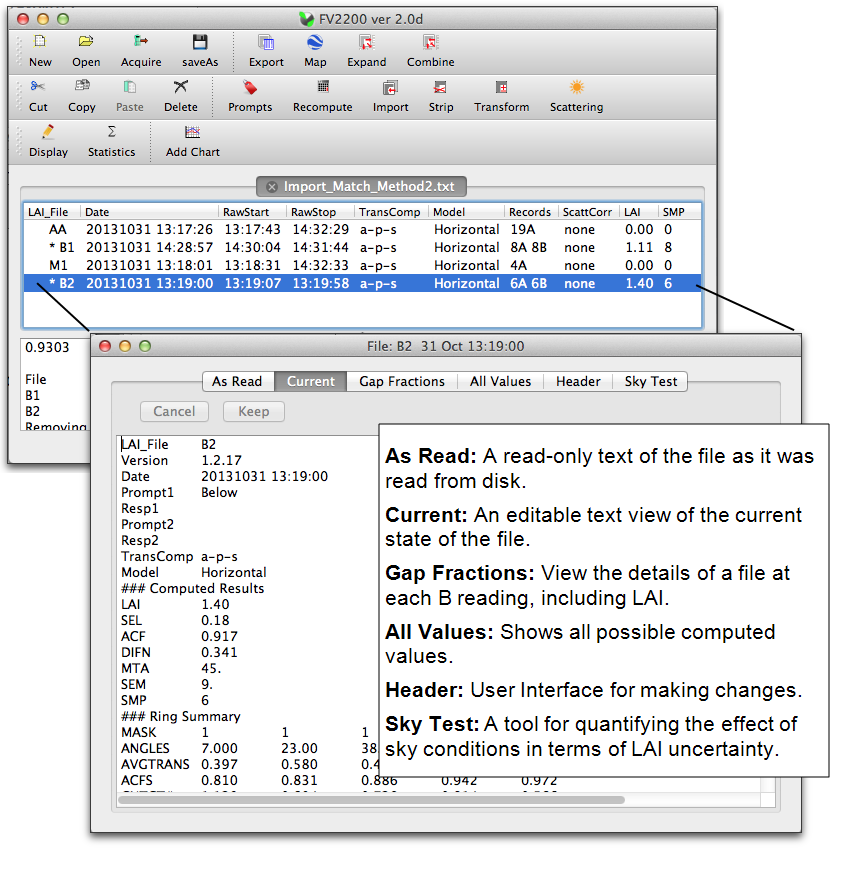
Double click a file in a view to open the Details window.
Import A Records
When A and B records are in separate files, they must be merged to compute results. If the A and B readings were collected using two different sensors, imported A records may also need to be adjusted to match the B sensor's calibration, if it hadn’t been done already. This is discussed in Multiple-Sensor Operation Revisited. Both of these tasks—importing and (if necessary) adjusting—are accomplished using the "Import Records" dialog.
Recompute Data Files
There are a number of reasons a file might need to be recomputed, such as adding scattering corrections, importing A readings, masking a ring, etc., and generally the recomputation happens automatically as part of that process. There is also a Recompute dialog box that lets you make some typical modifications (change the ring mask, change how transmittances are computed, or change the canopy model) and apply those changes to one or a group of files.
Implementing Scattering Corrections
Scattering corrections are discussed in Dealing with Scattering. If the necessary data (the K record precursors) have been collected for your files, use FV2200’s Scattering Tool to complete the task: generate K records, copy them to other files (if necessary), set the remaining inputs in the files, and recompute. The example given in Example 4 - Forest Sites with One Sensor (and Control Unit) includes all of these steps.
Plot Selected Data
You can plot data within an LAI file, or across multiple files. You can define a chart, then click on various LAI file(s) to update the chart for that file(s). All of this is configured using the Add Chart dialog.
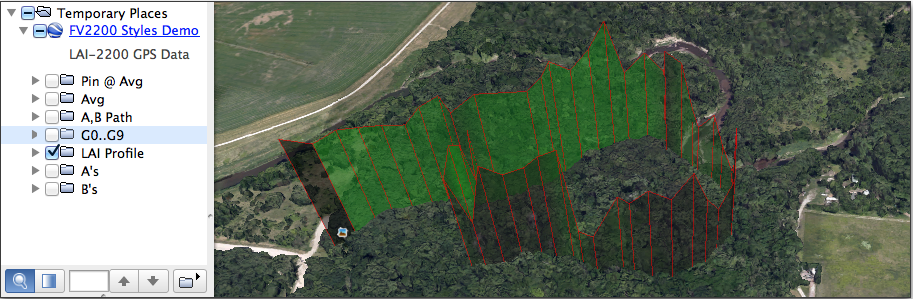
Make a GPS Plot
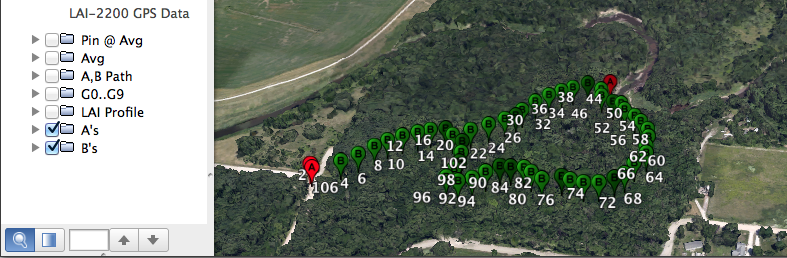
LAI files that contain GPS data, either because they were logged with an LAI-2200C console with built-in GPS, or they have had GPS data added as part of the scattering correction inputs, can be used to generate .kml files, which allows selected data to be displayed on a satellite image of the area. For example, Figure G‑1 shows a path of where the data points were logged (top) and a 3D image of LAI along that path (height being proportional to LAI at any given point).
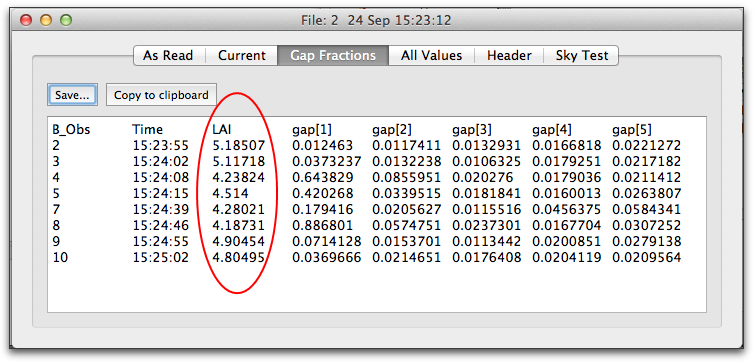
View LAI for each B Record
Often it is desired to “break apart” an LAI data file and see what the LAI was at each location for which there was a B reading. FV2200 version 2 provides this information for you without your having to do anything. To see it, double click the file to get the Details view, and click on the Gap Fractions tab.